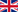
Toothfish (Chilean Seabass) |
|
| Scientific Name: | Dissostichus eleginoides (Patagonian Toothfish), Dissostichus mawsoni (Antarctic Toothfish) |
| Also known as: | Mero (Japan), Chilean Seabass (USA & Canada), Merluza Negra (Argentina), Bacalao de Profundidad (Chile) and Legine Australe (France). |
| Description: |
Toothfish can grow to over 2 metres in length and weigh up to 150kg. Toothfish are caught using mainly bottom-set longlines in depths of 1,200–2,200 metres. Commercial Patagonian toothfish fisheries began in the late 1980s off the coasts of Chile and Argentina, including the Falkland Islands. Over time, fisheries began further eastwards via South Georgia, Bouvet Island, Prince Edwards and Marion Islands, Crozet Island, Kerguelen Island, Heard Island and McDonald Islands, as well as Macquarie Island. There are also artisanal fisheries for Patagonian toothfish off the continental slopes of Chile, Argentina and Uruguay. The Antarctic toothfish fishery began later, as the fish tend to be found only in very southern latitudes and alongside the Antarctica icepack. The main legal fishery for Antarctic toothfish is in the Ross Sea, in FAO Divisions 88.1 and 88.2. Click here to read a FAQ document regarding Antarctic toothfish and the Ross Sea. Commercial fishing of toothfish is managed by the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) inside the CCAMLR Convention Area which spans the Antarctic Continent between 45 and 60 degrees South. Some fisheries inside territorial waters within the Convention Area (e.g. Crozet Island, Prince Edwards and Marion Islands) are managed separately by countries with territorial waters taking CCAMLR management practices into account. Toothfish fisheries outside the CCAMLR Convention Area in the coastal waters of Argentina, Chile and Uruguay are managed by the relevant coastal state. However, these fisheries are still subject to the CCAMLR Catch Documentation Scheme (CDS) which tracks the trade of toothfish from the point of unloading to the point of final consumption. |
| Characteristics: | White flesh, medium to firm texture, very high oil content. Highly sought after in fine dining restaurants. |
| Main Season: |
Dissostichus mawsoni (Antarctic Toothfish) are caught in summer months (January-March) while the ice in the Ross Sea has receded. Dissostichus eleginoides (Patagonian Toothfish) are caught in a number of different fisheries and the catching periods vary from area to area. |